Combining Array Tomography (AT) and STED for studying Alzheimer’s diseases
Cell Biophysics & Physical BiologyProject description
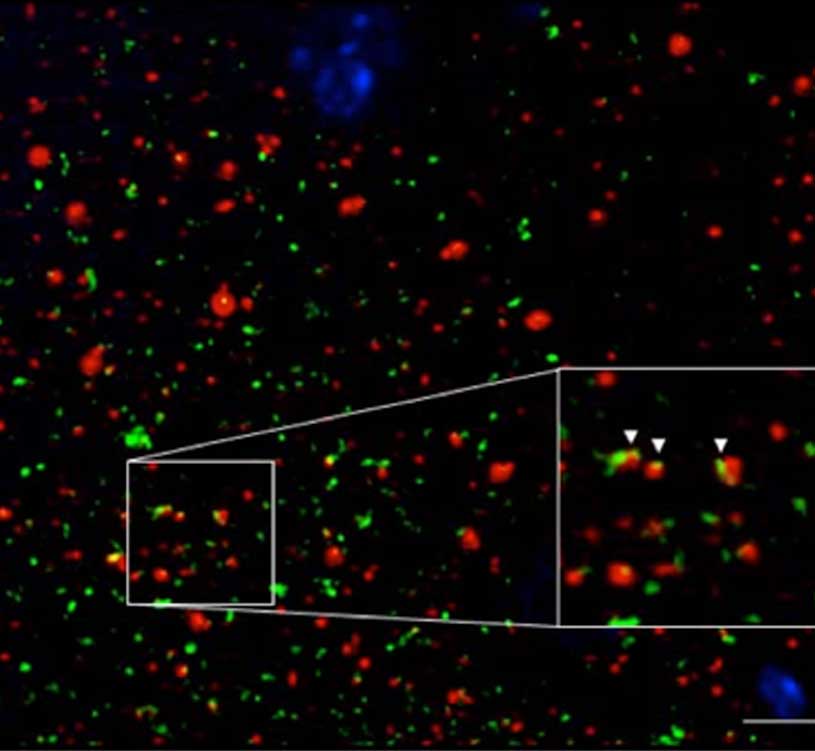
Synapses represent the main interaction structures between neurons in the central nervous system. The study of human synapses has been limited by its small size, being a typical cortical human synapse around 200nm. Array Tomography (AT) consists in physically sectioning 70nm-thin acrylic resin embedded tissue, in series of ribbons that can be stained and imaged with enhanced axial resolution. In this project we will combine Stimulated Emission Depletion (STED) and AT for the study of human synapses. Our objective is to achieve a voxel of 70x70x70nm with even enhanced resolution.
In this project we will investigate aggregates of Aβ peptide in human brain tissue from Alzheimer’s disease (AD). We will concentrate on the most toxic forms of Aβ, called Abeta oligomers (oAβ) that have been found surrounding plaques and depositing in synapses.
ICFO groups associated with the project
ICFO publications associated with the project
No publications associated to this project
External collaborations
Fundació Institut de Recerca de l’Hospital de Sant Pau (IRHSCP)
Funding
Internal