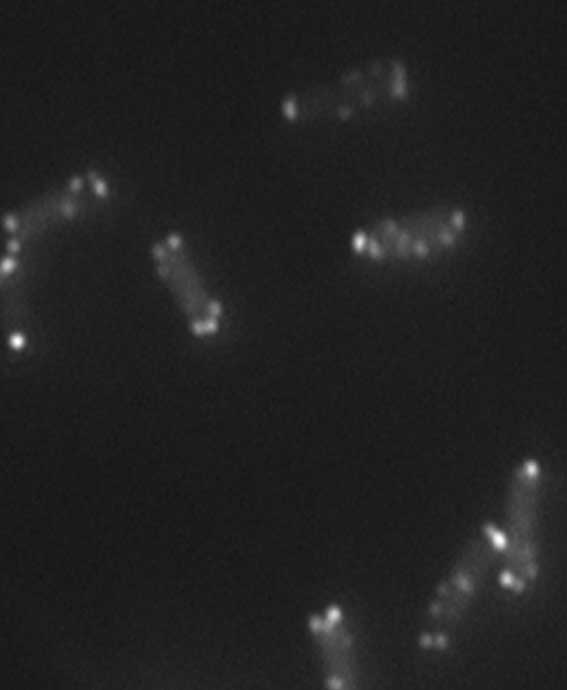
Colocalization of RecA and CheW proteins at Salmonella enterica
Cell Biophysics & Physical BiologyProject description
The RecA protein is a multifunctional protein that has been associated to Salmonella enterica swarming motility. Swarming is a flagellar-driven multicellular motility associated with bacterial virulence. It has been described that RecA interacts in vitro with CheW protein, the coupling protein that is essential for the polar chemoreceptor cluster formation. To deepen in the understanding of RecA and CheW relation, and to define the role of RecA in polar cluster structuration, it is essential to determine the location of the RecA and CheW inside the bacterial cell and quantify its interaction
The main objective of the present Project is the use of Stochastic Optical Reconstruction Microscopy (STORM) to unequivocally confirm and quantify the location and interaction of RecA and CheW at the S. enterica cell poles
ICFO groups associated with the project
ICFO publications associated with the project
No publications associated to this project
External collaborations
Departament de Genètica i de Microbiologia, UAB
Funding
Internal